Minimally invasive coronary artery bypass
Bypass surgery is a heart operation in which narrowed or closed coronary vessels are bypassed by introducing healthy blood vessels. Bypass surgery is one of the most common procedures in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. It is performed in the late stages of diseases, such as obliterating peripheral vascular disease, coronary heart disease, or in a post-infarction condition.
When is surgery necessary?
A bypass operation is necessary if one or more coronary arteries are strongly compressed or closed, and there is a significant violation of the blood circulation of the heart. Often this problem goes so far that drug treatment or balloon dilatation of vasoconstriction becomes ineffective. In such cases, the narrowed areas can be eliminated using the bypass operation. As a result, the duration and quality of life of a cardiological patient can be improved.
In 90% of the operated patients, significant relief or disappearance of complaints of angina pectoris is observed. However, if the patient is offered a bypass surgery, it is also necessary to weigh the chances of success of the treatment. Since this is a stressful procedure, the benefits and risks should be carefully evaluated by a cardiologist and cardiac surgeon.
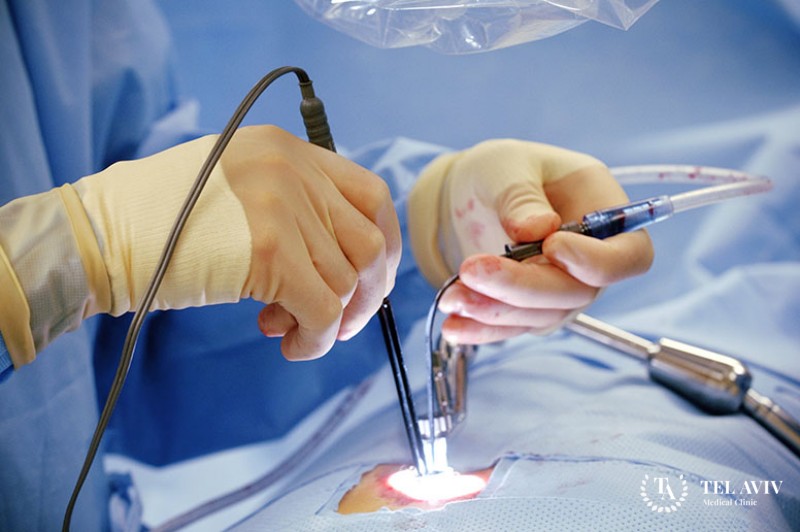
How minimally invasive bypass surgery is performed?
The leading Israeli clinic Tel Aviv Medical Clinic employs professionals who have vast practical experience and knowledge. We use unique methods of therapy and modern equipment. Our staff undergoes special training annually in leading foreign research centres. The specialist performs the bypass procedure in two techniques MIDCAB and OPCAB.
With the MIDCAB technique, the sternum is not opened, but access to the heart is achieved through an incision between the ribs on the left side of the chest. However, with this minimally invasive bypass operation, only coronary vessels of the anterior heart wall can be achieved.
With the OPCAB technique, access to the heart occurs through a sternum incision, but without the use of a cardiopulmonary bypass. As a rule, with this method, the coronary arteries of the posterior wall of the heart can be achieved. However, during the operation, the pumping power of the heart may be impaired if it is removed from its position, which requires the use of a cardiopulmonary bypass.


